
How to File Income Tax in Malaysia
Are You Hiring?
Find candidates in 72 Hours with 5+ million talents in Maukerja Malaysia & Ricebowl using Job Ads.
Hire NowEvery year, income tax filing becomes a key responsibility for millions of Malaysians. While employees are required to submit their own tax returns, employers and HR teams play an important supporting role in ensuring the process runs smoothly. Understanding how income tax filing works helps organisations reduce compliance risks, support employees better, and avoid unnecessary disputes during tax season.
Malaysia’s income tax filing process is now fully digital and managed through MyTax and the e-Filing platform operated by Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri Malaysia (LHDNM).
Who Needs to File Income Tax in Malaysia
Income tax filing is not limited to salaried employees. In general, individuals are required to file income tax if they fall within any of the following categories:
-
Salaried employees earning above the taxable threshold
-
Individuals earning more than RM37,333 annually after EPF deductions
-
Freelancers and gig workers, including e-hailing drivers and delivery riders
-
Self-employed individuals and business owners
-
Individuals who have been registered with LHDNM and issued a tax number
-
Employees with multiple income sources, such as salary plus rental or freelance income
Even if no tax is ultimately payable, individuals with an active tax file may still be required to submit a return.
Income Tax Filing Deadline in Malaysia
Income tax is assessed annually based on the calendar year. The common filing period is March to April for most individual taxpayers
e-Filing offers a longer submission window compared to manual filing, which is why it is strongly encouraged by LHDNM.
Late submission may result in penalties or fines, depending on the severity and duration of the delay. Employers should encourage employees to file early to avoid last-minute issues.
Essential Documents Needed for Tax Filing
Before filing income tax, individuals should gather all relevant documents to ensure accurate reporting.
Commonly required documents include:
-
EA Form, issued by the employer
-
EPF contribution statement
-
Insurance and takaful statements
-
Lifestyle-related receipts (devices, education, medical expenses, etc.)
-
Donation receipts (if applicable)
-
Business income and expense records for freelancers or self-employed individuals
Important: All receipts and supporting documents must be kept for at least seven (7) years, as required by LHDNM for audit purposes.
How to Register Income Tax Number with LHDNM
Individuals who are filing income tax for the first time must first register for a tax file number. Registration is done online through MyTax via the e-Daftar system. This applies to:
-
New employees
-
Freelancers and self-employed individuals
-
Anyone who has never been issued a tax number
Once registered and approved, LHDNM will issue a Tax Identification Number, which is required before any tax return can be submitted.
How to File Income Tax in Malaysia (MyTax e-Filing)
Income tax filing is completed through the MyTax e-Filing system.
The general process includes:
-
Log in to MyTax
-
Select the correct tax form (BE, B, or others depending on income type)
-
Enter employment income based on the EA Form
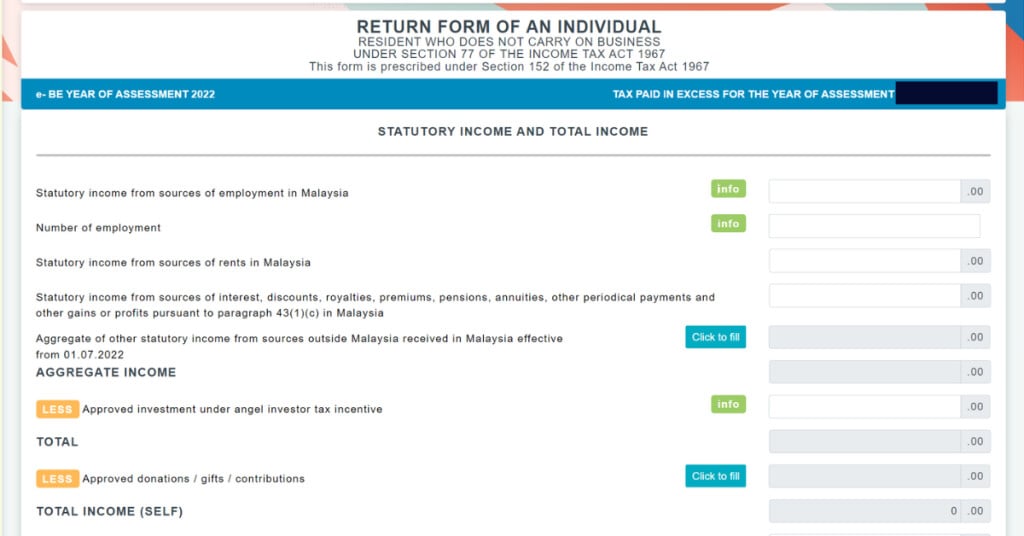
-
Declare other income sources, if any
-
Claim eligible tax reliefs

-
Review the tax summary

-
Submit the return
-
Save the acknowledgement slip for records

From an HR perspective, it is critical that payroll data and EA Forms issued to employees match the records submitted to LHDNM.
Types of Income: Taxable vs Exempt
Not all income is taxable under Malaysian tax law.
Common Taxable Income
-
Salary and wages
-
Bonuses and commissions
-
Fixed allowances
-
Business and freelance income
-
Rental income
-
Overseas interest income brought into Malaysia
Common Tax-Exempt Income
-
Dividends from Malaysian companies
-
EPF dividends
-
Hibah and inheritance
-
Gifts not related to employment
-
Certain government allowances
Understanding this distinction helps reduce reporting errors and unnecessary overpayment.
Tax Reliefs Malaysians Can Claim
Tax reliefs are designed to reduce chargeable income, which in turn lowers the total tax payable. Common relief categories include:
-
Individual relief
-
Spouse and child relief
-
Lifestyle purchases
-
Medical expenses
-
Education fees
-
Approved donations
Relief limits and eligibility may change from year to year. Taxpayers should always refer to the official LHDNM relief list for the latest updates.
EPF & Life Insurance Tax Relief (Important Section)
EPF-related reliefs are among the most commonly claimed deductions.
EPF and Life Insurance Relief Limits
-
EPF contributions: up to RM4,000
-
Life insurance or takaful premiums: up to RM3,000
-
Combined maximum relief: RM7,000
Need to check your tax relief total? Just use our EPF & insurance relief calculator.
 (2).jpg)
For Pensionable Public Servants
Pensionable public servants may claim life insurance premiums and voluntary EPF contributions under the allowed relief categories.
i-Lindung EPF Insurance
Insurance or takaful plans purchased through the i-Lindung platform may qualify under life insurance relief, subject to LHDNM approval.
EPF Dividends
Dividends earned on EPF savings are fully tax-exempt and do not need to be declared as income.
Common Tax Filing Mistakes to Avoid
Mistakes during tax filing can trigger audits or penalties. Common issues include:
-
Failing to declare all income sources
-
Using incorrect EA Form details
-
Claiming reliefs without valid receipts
-
Overclaiming tax relief amounts
-
Not keeping records for seven years
-
Submitting tax returns after the deadline
Employers can help reduce these errors by issuing accurate payroll documentation on time.
Why This Matters for HR & Employers
Income tax filing is not just an individual responsibility. Employers play a critical supporting role. For HR and employers, accurate tax processes:
-
Ensure EA Forms are correct and consistent
-
Reduce employee tax disputes
-
Improve compliance during audits
-
Build employee trust and confidence
-
Support smoother tax season communication
When payroll data aligns with MyTax records, both employers and employees benefit.
External References
For official guidance and updates:
FAQs
Who must file income tax in Malaysia?
Individuals earning above the taxable threshold or registered with LHDNM.
How do I file income tax for the first time?
Register for a tax number via e-Daftar and submit your return through MyTax e-Filing.
What documents are required for e-Filing?
EA Form, EPF statement, insurance records, receipts for reliefs, and income records.
How much EPF contribution is tax-deductible?
Up to RM4,000 for EPF contributions, with a combined EPF and life insurance relief of up to RM7,000.
What happens if income tax is filed late?
Late filing may result in penalties or fines imposed by LHDNM.
Looking to Hire or Expand Your Team?
AJobThing helps you post job ads and reach more candidates efficiently.
Read More:
-
Penyata KWSP: How to Check, Download & Understand Your EPF Statement
-
SST 2026 Malaysia: Key Changes, Tax Rates and Employer Compliance Guide
-
EIS Contribution Table 2026 Malaysia – Rates, Salary Ceiling and Calculation Guide
-
Malaysia Employment Pass Salary Increase 2026 Takes Effect on 1 June
-
Malaysia Income Tax Exemption 2025 Guide for Employers & HR | e-Filling 2026
-
LHDN Stamp Duty Requirements for Business and Employment Documents in Malaysia
-
What Employers Must Submit Through LHDN e-Filing in Malaysia
-
i-Topup KWSP: Contribution Rules & Guide for Employers in Malaysia
-
i-Simpan EPF (KWSP): How It Works & How Employees Can Contribute
-
EPF (KWSP) New Updates in January 2026 for Employers & HR in Malaysia
-
Penamaan KWSP in Malaysia: Legal Implications, Process, and HR’s Role
-
i-Sayang KWSP Guide: Requirements, Benefits & How to Register
-
EPF, SOCSO, EIS, and LHDN Employer Registration Guide for Malaysian Companies
- Cara Kira Potongan KWSP dan SOCSO | How to Calculate EPF and SOCSO Deductions in Malaysia
-
Deadlines & Penalties for SOCSO, EPF, PCB/Form E, and HRD Levy in Malaysia
-
EPF Withdrawal for Education: Employer’s Guide to Supporting Staff
-
Akaun Fleksibel (EPF’s New Account Structure): Key Info for Employers
-
KWSP Call Centre for Employers: Contact Numbers, Services, and Support Channels

